test for.cuff tear|rotator cuff tear diagnosis : exporters Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as .
Request Deletion - Letsgab - Porn Photos & Videos - EroMe
{plog:ftitle_list}
Keyboard: Use and arrow keys to navigate on next/previous pages. Mouse: Click on the left or right side of the page to navigate on next/previous pages.
They'll also test the strength of the muscles around your shoulder and in your arms. Imaging tests may include: X-rays. Although a rotator cuff tear won't show up on an X .
A doctor or physiotherapist can use one of more than 25 functional tests during a physical exam to diagnosis a torn rotator cuff. Some of these tests directly indicate a rotator cuff. summary. Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. . Rotator Cuff Tear. A partial or complete rotator cuff tear makes it difficult to raise and move your arm. You may have shoulder pain and arm weakness. Rotator cuff injuries are .
Special testing is generally performed following a full examination of the shoulder that includes but is not limited to patient history, mechanism of injury, clinical observation, bony and soft tissue palpation, assessment of active and passive .
Your doctor may recommend a diagnostic imaging study such as a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan or ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment of a rotator cuff tear may prevent symptoms such as .If you fall down on your outstretched arm or lift something too heavy with a jerking motion, you can tear your rotator cuff. This type of tear can occur with other injuries, such as a broken collarbone, a dislocated shoulder, or a wrist fracture.To enhance the ability to detect full-thickness rotator cuff tears, a test-item cluster has been developed. A cluster improves the post-test probability for the clinical diagnosis of a full-thickness tear.
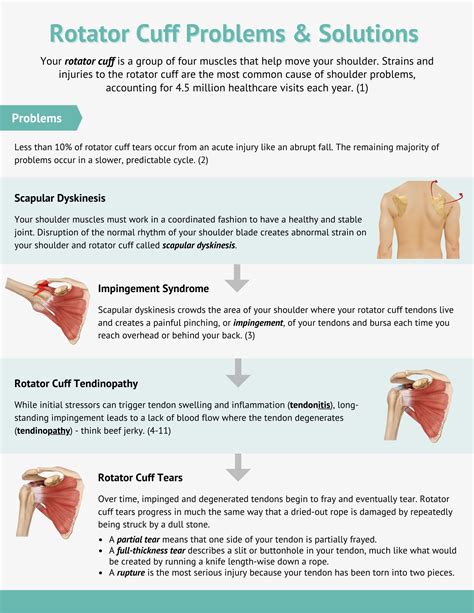
Print. Rotator cuff tears are a common injury of the shoulder joint. The range of motion of your shoulder—the amount of movement at the joint—is greater than any other joint in the body. The rotator cuff has several roles. It is . Rotator cuff tears are a very common source of shoulder pain and decreased motion that can occur due to both traumatic injuries in young patients as well as degenerative disease in the elderly patient. Diagnosis can .
Purpose [edit | edit source]. The drop arm test is used to assess for full thickness rotator cuff tears, particularly of the supraspinatus.This can be useful when diagnosing sub-acromial pain syndrome (shoulder impingment) or to differentiate between shoulder and rotator cuff pathologies.The drop arm test may be more accurate when used in a battery of tests such as:
Epidemiology. In adults, rotator cuff injury is the most common tendon injury seen and treated. Statistically, approximately 30% of adults age over 60 have a tear, and 62% of adults over 80 have tears. In Germany, a prospective study on 411 asymptomatic shoulders demonstrated a 23% overall prevalence of RC tears with 31% in those of age 70 and 51% in .To test the presence of a shoulder full-thickness rotator cuff tear using the Drop-Arm Sign, Painful Arc Sign, and the Infraspinatus Muscle Test. Evidence [ edit | edit source ] Based on the Park et al [1] study, the combination of the following 3 special tests have produced the highest post-test probability to diagnose a full-thickness rotator .Rotator cuff injuries are among the most common causes of shoulder pain. These can manifest as bursitis, tendonitis or tendon tears. The patients usually complain of pain and reduced function of the affected shoulder. In young patients a rotator cuff tear is usually traumatic in etiology and the symptoms show an acute onset. Rotator cuff tears may cause pain and limit your ability to do daily tasks. Or, a rotator cuff tear may cause no pain for some time. If you suspect you have a rotator cuff tear, reach out to your healthcare provider for advice. Most of the time, non-invasive measures can help restore shoulder function and reduce pain.
A rotator cuff tear is a rip in the muscles stabilizing your shoulder. Explore symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and prevention tips to manage and recover effectively.
torn rotator cuff test results
Rotator cuff tears, glenohumeral joint instabilities, and labral tears are associated with an increased incidence of subacromial impingement (1). The "cluster" of tests validated to rule in/rule out subacromial impingement only indicates the presence or absence of impingement (1). . The best combination of tests to detect a full-thickness RTC .
This is the most common way to diagnose a rotator cuff tear and what type of tear it is. MRI results can provide information about the tear that can help the provider make certain decisions .Disuse atrophy may be present in chronic tears; TTP lateral aspect of upper arm or in subacromial region; Rotator Cuff Tests. Supraspinatus Test (+ LR 3.2) Abduct arm to 90', forward flex it 30' with thumb down ("empty beer can position") Test for pain/weakness against resistance to continued abduction; Infraspinatus and Teres Minor TestThis type of shoulder test, or rotator cuff injury test, is used to identify tears within the muscle group of the rotator cuff. Shoulder Shrug Test; This torn rotator cuff test checks if the patient imitates a shrug movement when trying to actively raise their arm. The patient is unable to raise the arm to a 90 degree elevation without raising .
Rotator cuff injury test types. Which tests are performed may depend, in part, on whether your suspected rotator cuff injury is in the supraspinatus, subscapularis, or infraspinatus. and to determine whether the tendons that lie between the humerus and the acromion are being pinched .
Finally, the “painful arc sign” has high sensitivity (97.5 percent) as a single finding, making it helpful in ruling out rotator cuff tears when absent. 2 The test is performed by having the . most specific test for full thickness rotator cuff tear (specificity 98%) Infraspinatus. Infraspinatus Strength. technique. with the pateint's elbow in 90 degrees flexion, the arm at the side and internally rotated 45 degrees, external rotation strength can be checked against resistance by the examiner.Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). .Symptoms of Partial Rotator Cuff Tears. Not all patients with partial rotator cuff tears have symptoms, but those who do may experience pain in the shoulder. Generally, the most painful motion with a partial rotator cuff tear is lifting things over the shoulder level or far away from the body. Lifting in this manner is very stressful on the .
A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient slowly lowers the arm to .A supraspinatus tear is a tear or rupture of the tendon of the supraspinatus muscle. The supraspinatus is part of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. Most of the time, it is accompanied by another rotator cuff muscle tear.This can occur due to trauma or repeated micro-trauma and present as a partial or full-thickness tear. Quite often, the tear occurs in the tendon or as an .腱板断裂 Rotator cuff tear. . ISP test: 棘下筋および小円筋の評価では,患者に肘を90度に屈曲した状態で腕を体側につけさせ,抵抗に対して外旋するように促す;この姿勢は,肩腱板の筋肉機能を他の筋肉(例,三角筋)機能から孤立させる。このテストで筋力 .
The O’Brien test can help diagnose a tear in the top or superior part of your labrum. A superior labrum tear is also called a SLAP tear, which stands for superior labrum, anterior to posterior. The O’Brien test can also rule out other problems, such as: Rotator cuff tear. Shoulder impingement syndrome. For many years the single contrast shoulder arthrogram has been the standard technique for diagnosing rotator cuff tears. In this test contrast material is injected into the glenohumeral joint (see figure 18); after brief exercise radiographs are taken to reveal intravasation of the dye into the tendon (see figures 18 and 19) or extravasation . The rotator cuff is a group of muscles critical for the strength, stability and function of the shoulder. Tears of the rotator cuff tendons are a common source of shoulder pain, weakness and other problems. Imaging studies, such as radiographs, MRIs or ultrasounds, are used to evaluate rotator cuff tears. Physical therapy and the occasional use of cortisone .Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16.
What causes rotator cuff tears? There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and wear. Injury. If you fall down on your outstretched arm or lift something too heavy with a jerking motion, you could tear your rotator cuff. This type of tear can occur with other shoulder injuries, such as a broken collarbone or dislocated shoulder. Wear. Rotator cuff tear is one of the most common shoulder diseases. It is interesting that some rotator cuff tears are symptomatic, whereas others are asymptomatic. Pain is the most common symptom of patients with a tear. . The lift-off test to detect a subscapularis tear was introduced by Gerber and Krushell . The rotator cuff can also be strained or tear after a fall, a car accident, or another sudden injury. These injuries typically cause intense and immediate pain. What are the symptoms of rotator . Drop Arm Test. This simple test assesses the possibility of a rotator cuff tear. During the test, the patient (either sitting or standing) holds their arm straight out at a 90 degree angle, then slowly lowers the arm down to their side. The provider is looking for the patient’s ability to raise and lower the arm in a controlled manner.
torn rotator cuff test procedure
webHannah Owo | Scrolller . Hannah Owo
test for.cuff tear|rotator cuff tear diagnosis